In Oracle General basic accounts are classified into 5 types –
• Asset
• Expense
• Liability
• Ownership/Stockholders Equity
• Revenue
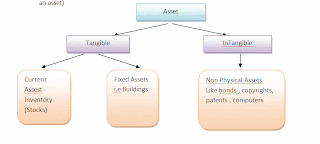
1) Assets - In financial accounting, assets are economic resources. Anything tangible or intangible that is capable of being owned or controlled to produce value and that is held to have positive economic value is considered an asset. Simply stated, assets represent ownership of value that can be converted into cash (although cash itself is also considered an asset)
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholder's Equity (Owner's Equity)
$945 = $500 + $445
For example: A student buys a computer for $945. This student borrowed $500 from his best friend and spent another $445 earned from his part-time job. Now his assets are worth $945, liabilities are $500, and equity $445 (Example is Used throughout document)
Current Assets - Current assets are cash and other assets expected to be converted to cash, sold, or consumed either in a year or in the operating cycle (whichever is shorter), without disturbing the normal operations of a business
1. Cash and cash equivalents — it is the most liquid asset, which includes currency, deposit accounts, and negotiable instruments (e.g., money orders, cheque, bank drafts).
2. Short-term investments — include securities bought and held for sale in the near future to generate income on short-term price differences (trading securities).
3. Receivables — usually reported as net of allowance for uncollectable accounts.
4. Inventory — trading these assets is a normal business of a company. The inventory value reported on the balance sheet is usually the historical cost or fair market value, whichever is lower. This is known as the "lower of cost or market" rule.
5. Prepaid expenses — these are expenses paid in cash and recorded as assets before they are used or consumed (a common example is insurance). See also adjusting entries.
2) Liability (financial accounting) - In financial accounting, a liability is defined as an obligation of an entity arising from past transactions or events, the settlement of which may result in the transfer or use of assets, provision of services or other yielding of economic benefits in the future. If you stick with these two thoughts (“owe” and “pay someone in the future”), you should be able to easily identify your liabilities.
A liability is defined by the following characteristics:
• Any type of borrowing from persons or banks for improving a business or personal income that is payable during short or long time;
• A duty or responsibility to others that entails settlement by future transfer or use of assets, provision of services, or other transaction yielding an economic benefit, at a specified or determinable date, on occurrence of a specified event, or on demand;
• A duty or responsibility that obligates the entity to another, leaving it little or no discretion to avoid settlement; and,
• A transaction or event obligating the entity that has already occurred
Common Liability Accounts ( Payables ):
Current Liabilities:
• Notes Payable - Promissory notes to creditors.
• Accounts Payable - What you owe others on account.
• Unearned Revenue - You've been paid, but haven't delivered.
• Salaries Payable - Salaries you owe employees.
• Interest Payable - Interest you owe.
• Taxes Payable - Taxes you owe.
Liabilities = Assets - Stockholder's Equity (Owner's Equity)
$500 = $945 - $445
Owner's (Stockholders') Equity –
Stockholder's Equity (Owner's Equity) = Assets - Liabilities
Expense - In common usage, an expense or expenditure is an outflow of money to another person or group to pay for an item or service, or for a category of costs. For a tenant, rent is an expense. For students or parents, tuition is an expense. Buying food, clothing, furniture or an automobile is often referred to as an expense. An expense is a cost that is "paid" or "remitted", usually in exchange for something of value.
In accounting, expense has a very specific meaning. It is an outflow of cash or other valuable assets from a person or company to another person or company. This outflow of cash is generally one side of a trade for products or services that have equal or better current or future value to the buyer than to the seller. Technically, an expense is an event in which an asset is used up or a liability is incurred.
Ex.
41101 COGS - Domestic Sales ( Cost Of goods Sold In Inventory )
41111 COGS - Clearance Sales
51105 Petrol Allowance
51107 Fixed OT
51121 Absence Salary Deduction
51151 Overtime - I
A Query -
select FLEX_VALUE_MEANING , DESCRIPTION from FND_FLEX_VALUES_VL a
where FLEX_VALUE_MEANING in (select ACCOUNT from YKA_AFF_V b where GL_ACCOUNT_TYPE = 'E' and a.FLEX_VALUE_MEANING = b.ACCOUNT )
Debits and Credits
Generally these types of accounts are increased with a debit:
Dividends(Draws)
Expenses
Assets
Losses
You might think of D – E – A – L when recalling the accounts that are increased with a debit.
Generally these types of accounts are increased with a credit:
Gains
Income
Revenues
Liabilities
Stockholders' (Owner's) Equity
You might think of G – I – R – L – S when recalling the accounts that are increased with a credit.
A Small Example to understand Accounting -
A debit memo on a bank statement refers to a deduction from the bank account’s balance. In other words, a debit memo has the same effect as a check written on the bank account.
ReplyDeleteA bank debit memo could be a charge for interest owed to the bank, a loan payment, a fee owed for the printing of checks, a fee for the handling of a check that was returned because of insufficient funds, a transfer of funds from the bank account to another account at the bank, and so on.
The charge, decrease, or reduction is likely called a debit memo because the checking account balance is a liability on the bank’s books. This is the case because the bank has your money as one of its assets and it has your account balance as one of its liabilities. When the bank decreases your account balance, it is reducing its liability. Liabilities are reduced with a debit entry. That also explains why the bank credits your account when your account balance is increased.